Key Takeaways
- QLED TVs offer excellent color saturation and brighter panels at a lower price compared to OLED TVs.
- OLED TVs have nearly perfect black levels and contrast, faster pixel response times, and better viewing angles.
- QLED TVs are a better choice for brightly lit rooms with glare, while OLED TVs are ideal for gaming and rooms with minimal glare.
If you’ve shopped for a TV in the last decade, you’ve seen the words “QLED” and “OLED” all over the place. While the two acronyms look very similar and TVs with each type of technology can cost about the same, they are very different technologies. Knowing more about them can help you make a purchasing decision one way or the other.
Best 65-inch 4K Smart TV 2023: Amazing large Ultra HD TVs
When it comes to modern televisions, there’s an argument to be made that the bigger, the better. Here’s our pick of the best.
In this article, we’ll talk about what QLED and OLED are, how they work, and the pros and cons of each one. In general, though, OLED tends to be the higher quality screen technology, while QLED is generally available for less money. It gets more complex than that, however, so let’s get into it.
QLED vs OLED: What are they?
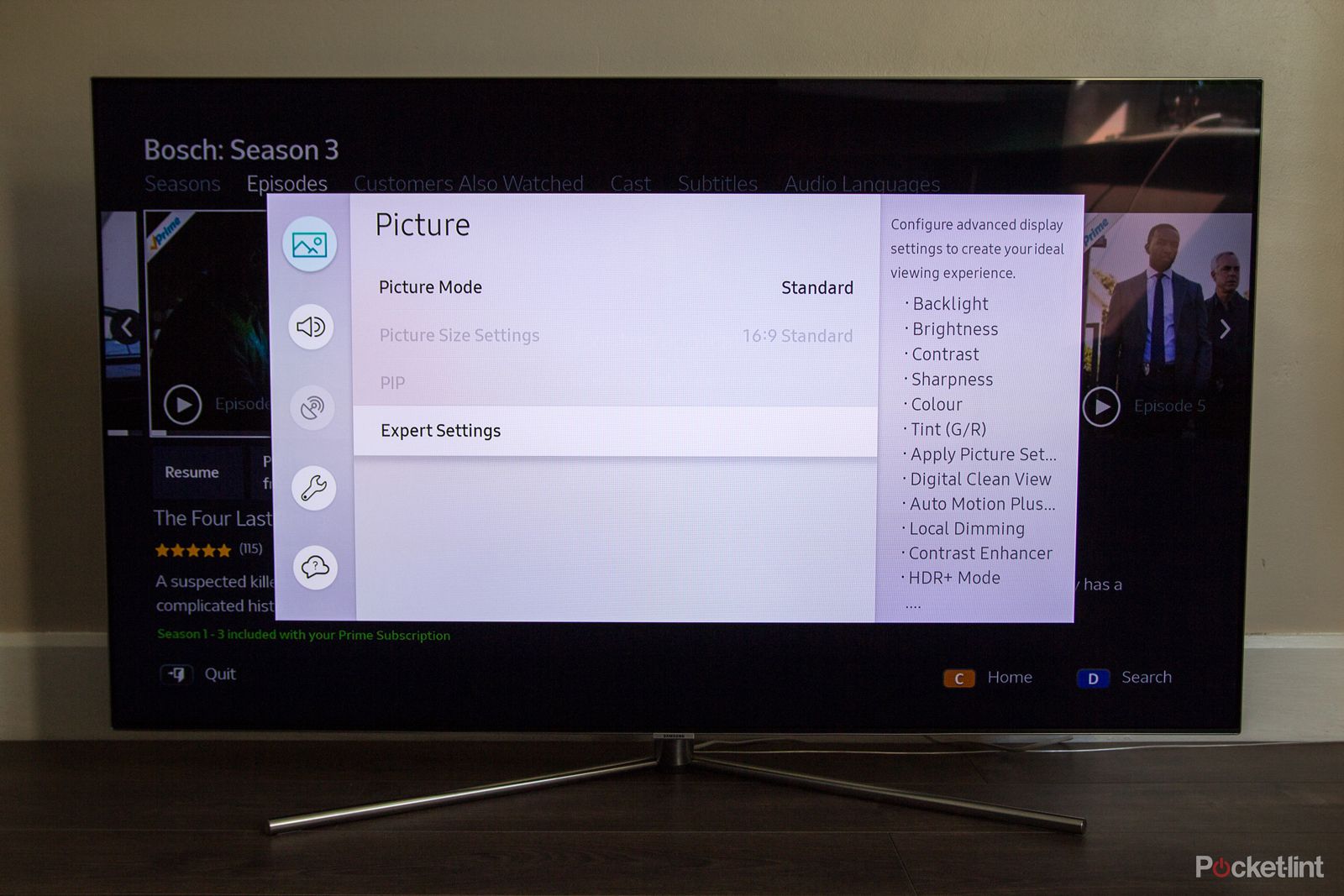
QLED is an acronym that stands for “Quantum Dot LED” and it’s the current generation of LED technology. It uses an extra layer of phosphorescent crystals, also known as nanocrystals, to improve a TV’s overall brightness and color saturation. It otherwise works the same as older LED TV technology.
Each TV maker’s implementation is slightly different, so you’ll see several different labels for this when shopping for TVs. For example, Samsung uses Neo QLED, like on the Samsung QN90C Neo QLED TV, as its branding for its own QLED technology. Rest assured that if you see QLED in the TV’s name, it simply means that it has that extra layer of crystals that help increase its saturation and brightness.
Netflix
OLED is another acronym that means “Organic LED” and it’s the most advanced TV technology there is right now. Each pixel is made from a material that lights up when it’s hit with a bit of electricity. Thus, each pixel is its own backlight and can light up independently of all the other pixels. This results in clean blacks, outstanding contrast, very low pixel response times, and better viewing angles.
Like QLED, every OLED TV manufacturer has a slightly different method of building these TVs. An example is the LG G3, which uses LG’s WOLED panels. Another is Samsung’s OLEDs, which use the company’s QD-OLED display. The underlying technology is the same. They just have slightly different implementations.
How do QLED TVs work?
QLED TVs work almost the same as a regular LED TV except they have the extra quantum dot layer for the light to travel through. LED TVs work by having a backlight of some sort. The light travels through the various layers inside the TV, including the liquid crystal (LCD) layer and the quantum dot layer. The viewer sees a picture based on how the light is passed through the layer.
The quantum dot layer is quite important here as it changes a few aspects of the TV. In QLED TVs, the backlight is typically blue instead of white. The blue light produces the blue you see on your TV set. When light passes through the quantum dots layer, the light refracts and changes to either red or green. The TV then mixes those colors together to produce the picture on your screen.
Since quantum dots don’t waste the energy from the TV’s blue light, it allows for a much more saturated red and green than you get from regular LED TVs, and the efficiency with which the light is refracted means that the TV is brighter overall. A quantum dot layer typically has billions of red and green dots, and it’s all somehow less expensive than OLED panels.
LG
How do OLED TVs work?
OLED TVs are both more and less complicated than QLED TVs. They are a solid-state semiconductor device comprised of several layers, including a substrate, anode, a conducting layer, an emissive layer, and multiple organic layers. The organic layers are where the “O” in OLED comes from. Unlike QLEDs, there is no backlight.
Generally speaking, OLED TVs use electrophosphorescence to emit light. The TV applies an electrical current that travels from the cathode to the anode layer, passing through the organic layers as it does. As all of this stuff passes through into the emissive layer, which causes the OLED to glow. The color depends on the organic layers and the brightness is determined by how much electricity is used.
There are several different types of OLED displays, with the biggest difference being the construction, order, and material choices of the various layers. For instance, WOLED panels, which LG uses in its OLED TVs, include color filters so that the panel can directly emit white light. Thus, instead of having RGB (red, green, and blue) subpixels, it has WRGB (white, red, green, and blue) subpixels.
QLED pros and cons
Pocket-lint
Like all things, there are good and bad things about QLED panels. For the below points, we’re comparing it directly to OLED panels. Also, these are generalized statements. Some manufacturers have brighter, more vivid displays than others.
QLED pros
- Generally less expensive than OLED panels.
- Excellent color saturation.
- Higher brightness ceiling.
- Larger number of available screen sizes.
- It has a longer expected lifespan and zero risk of permanent burn-in.
- A larger variety of options, although this depends on region.
QLED Cons
- Thicker than OLED panels.
- Less deep blacks and lower overall contrast ratio than OLED panels.
- Slower pixel refresh rates make them less good for gaming.
- Quality can vary wildly depending on backlight type, price range, and manufacturer. For example, mini-LED QLED TVs actually have respectable black levels and contrast, whereas cheaper, edge-lit panels can make blacks look gray and have noticeably worse contrast.
- QLED TVs tend to have less stutter, but more motion blur.
OLED pros and cons
LG
The same logic applies here. We’re comparing OLED panels directly to QLED panels.
OLED pros
- Nearly perfect black levels and contrast while still having excellent colors.
- Thinner than QLED panels
- Since OLED panels can turn black pixels off entirely, OLEDs typically use less power than QLED TVs.
- Better viewing angles.
- Better pixel response times, which reduces motion blur, makes it great for gaming.
- OLED TVs have no blooming. Blooming occurs when LED TV backlights cause bright objects on a dark background to have a halo of light.
OLED cons
- There is a risk of permanent burn-in. Technically, it’s more accurate to say burn-out. Each pixel is like a candle. Once you burn the metaphorical candle too much, it burns out, and causes permanent retention.
- OLEDs tend to have a shorter overall lifespan than LED TVs.
- They also tend to be more expensive.
- Not as good in bright rooms with lots of glare.
- OLED TVs tend to have less motion blur, but more stutter. Pick your poison.

The best smart TVs: Top picks from LG, Roku, and more
The best smart TVs add useful and expansive features to your entertainment set-up.
Is QLED or OLED better?
Blow-for-blow, OLEDs are the better TV technology. The ability to self-emit light from each individual pixel gives OLED advantages that QLED can’t replicate. After all, blacks on a TV don’t get any deeper than the light being entirely off, and pixel response times on OLEDs are crazy fast.
That isn’t to say that QLED is bad. It’s that LED TV technology hasn’t caught up to the natural advantages that OLED TVs have. QLED TVs have natural advantages as well, like no burn-in risk, longer lifespans, and brighter panels. However, it is much more difficult to get a deep black than it is to get a bright white.
Should you buy QLED or OLED?
It depends on a variety of factors, like budget, living room set up, and what kind of media you intend to consume with it. There is no easy answer, but we have a few guidelines you can follow.
Buy a QLED if you:
- Want the brightest possible picture with saturated colors.
- Are putting it in a brightly lit room with a lot of glare.
- Want to shop in a wider price range, or if you want a smaller TV.
- Are looking for a TV that will last you a long time.
- Don’t want anxiety about burn-in.
Buy an OLED if you:
- Want the highest possible contrast and the deepest possible blacks.
- Have a living room without a lot of glare.
- Intend on gaming with modern consoles like the Xbox Series X or the PlayStation 5.
- Don’t mind altering your habits a bit to prevent burn-in.
- Have the money for it.
Overall, the above are mostly guidelines. Hundreds of millions of people either currently game or have gamed on LED TVs and monitors without any issues. Other folks don’t feel the slightest bit of anxiety about burn-in for their OLED TVs and just enjoy having one. It ultimately comes down to what you’re looking for.
Plus, both technologies have been working on their flaws. Mini-LED TVs have better contrast and deeper black levels than prior LED TVs, and some can cost less than $1,000. Meanwhile, modern OLED TVs are made out of better materials to improve their lifespans and have automatic maintenance procedures that help prevent burn-in.
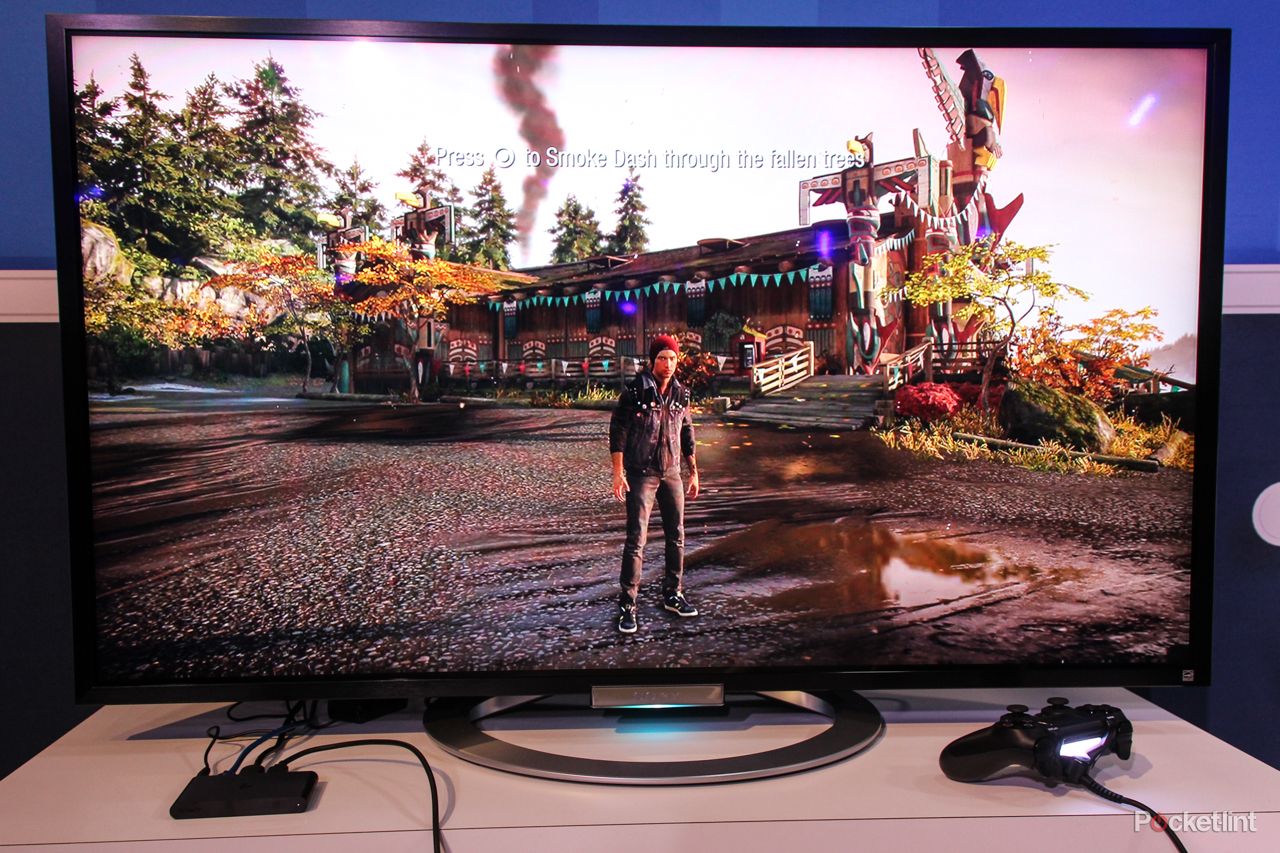
Why is OLED better for gaming?
The big answer here is pixel response times. Pixel response time is how long it takes for a pixel to go from one color to another. OLED TVs have nearly instant pixel response times, which means cleaner motion and movement in a video game environment. Add to that, the excellent picture quality, exceptionally high contrast, and generally low input lag, and OLED TVs just do it all well.
However, QLEDs aren’t exactly garbage by comparison. Many of them have perfectly reasonable pixel response times. They’ll still introduce some motion blur, but not nearly enough to make games unplayable or unpleasant. You can still play modern consoles on a QLED TV and be perfectly happy with it. OLEDs just do it measurably better.
Is QLED or OLED better for your eyes?
This is a very subjective question because there aren’t really any good academic studies about it, at least not yet. There isn’t likely a significant difference in terms of eye strain. However, different people are sensitive to different things.
For example, OLED TVs have more stutter but less motion blur thanks to their high pixel response times. QLED TVs have more motion blur, but less stutter. So, if you’re sensitive to motion blur, OLED is a better choice. If you’re sensitive to stutter, QLED is a better option.
QLEDs are also brighter, which works great in an already bright room. However, it may cause some discomfort if you don’t turn the brightness down at night when the room is much darker. OLEDs are much better for darker rooms, but you may strain to see things when the room is brightly lit.
It’s mostly about picking your poison. There is no definitive answer here and the Internet seems to be at odds regarding this question. Usually, that means there isn’t a big enough difference to matter.
Trending Products

Cooler Master MasterBox Q300L Micro-ATX Tower with Magnetic Design Dust Filter, Transparent Acrylic Side Panel, Adjustable I/O & Fully Ventilated Airflow, Black (MCB-Q300L-KANN-S00)

ASUS TUF Gaming GT301 ZAKU II Edition ATX mid-Tower Compact case with Tempered Glass Side Panel, Honeycomb Front Panel, 120mm Aura Addressable RGB Fan, Headphone Hanger,360mm Radiator, Gundam Edition

ASUS TUF Gaming GT501 Mid-Tower Computer Case for up to EATX Motherboards with USB 3.0 Front Panel Cases GT501/GRY/WITH Handle

be quiet! Pure Base 500DX ATX Mid Tower PC case | ARGB | 3 Pre-Installed Pure Wings 2 Fans | Tempered Glass Window | Black | BGW37

ASUS ROG Strix Helios GX601 White Edition RGB Mid-Tower Computer Case for ATX/EATX Motherboards with tempered glass, aluminum frame, GPU braces, 420mm radiator support and Aura Sync